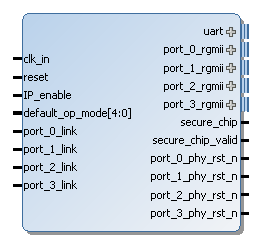
ManagedRedundantSwitch IP core (MRS) is a combination of SoC-e HSR-PRPSwitch (HPS) and ManagedEthernetSwitch (MES) IP cores offering a redundant Ethernet switch capability. The MES module is a non-blocking crossbar matrix that allows continuous transfers between all the ports. It implements Store&Forward switching approach in order to fulfill Ethernet standard policy regarding frame integrity checking each frame before forwarding them. On the other hand, the HPS module introduces HSR and PRP redundant capabilities in the ports that are required. HSR switching approach is Cut-Through.
Thus, the combination of MES and HPS offers the maximum performance and maximum compatibility with the standards.
MRS can be supported on the following Xilinx FPGA Families:
- 7-Series (Zynq, Spartan, Artix, Kintex, Virtex)
- Ultrascale (Kintex, Virtex)
- Ultrascale+ (Zynq MPSoC, Kintex, Virtex)
- Versal ACAP
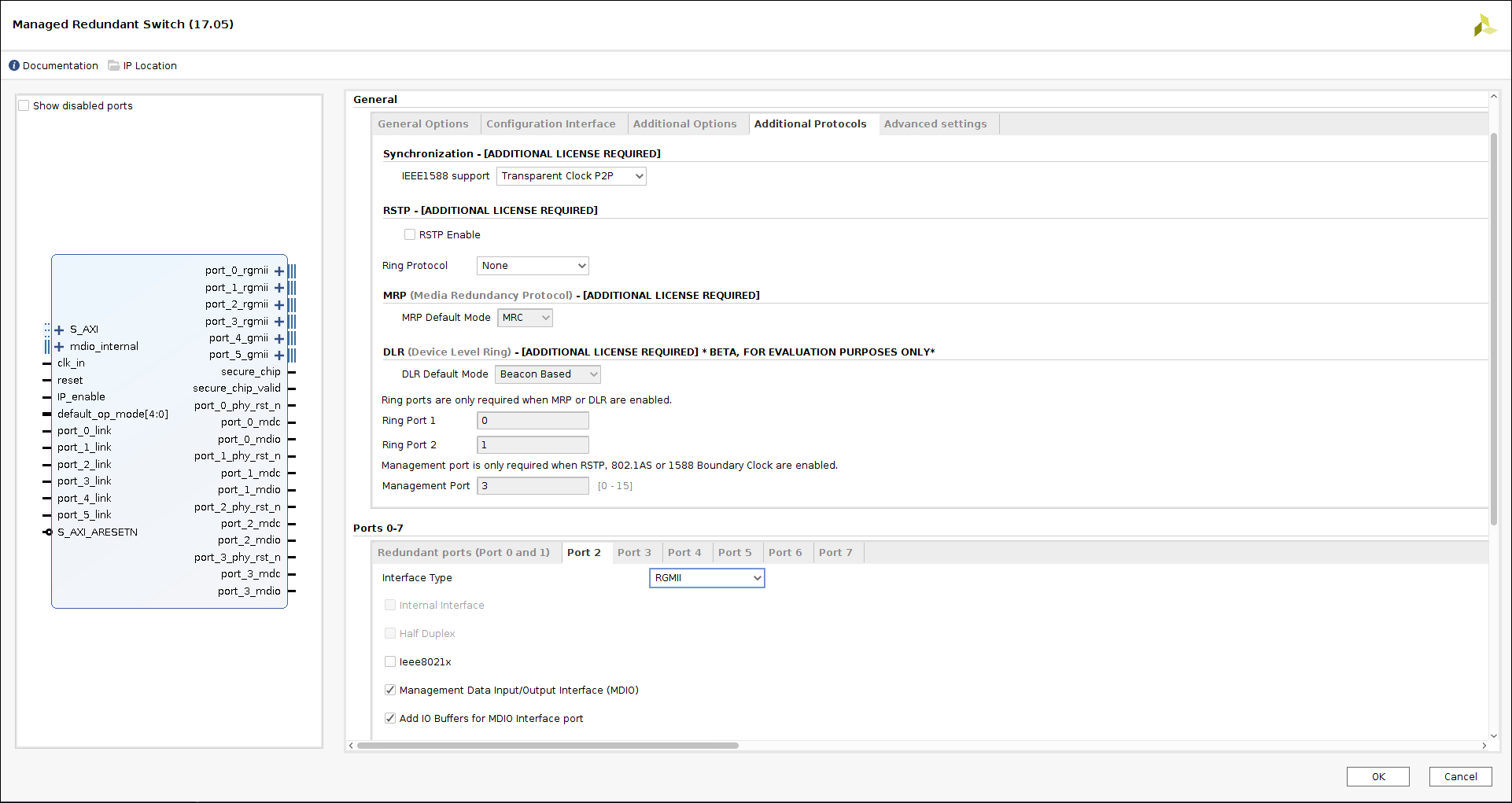
MRS is designed to be easily integrated in your FPGA designs by taking advantage of the new Xilinx Vivado Tool, that allows to use the IP Cores in a graphical user interface and configure IP parameters in an easy way.
Managed Redundant Switch IP Core key features:
Interfaces
- Full-duplex 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet Interfaces
- Half-duplex 10/100 Mbps Ethernet Interfaces
- Full-duplex 10 Gbps Ethernet Interfaces (Under Development)
- Configurable 3 to 16 Ethernet ports
- MII/GMII/RGMII/SGMII/QSGMII Physical Layer device (PHY) interfaces
- Different data rate supported for each port
- Copper and Fiber optic media interfaces: 10/100/1000Base-T, 100Base-FX, 1000Base-X
Switching
- Dynamic MAC Table with automatic MAC addresses learning and aging (up to 2048 entries)
- Static MAC Table (up to 2048 entries)
- Jumbo Frame Management
- Ethertype Based Switching
- Ingress Port Mirroring
- Broadcast/Multicast Storm Protection
- Per-Port Rate limiting (Broadcast, Multicast and Unicast traffic)
Time Synchronization
- IEEE 1588v2 Stateless Transparent Clock functionality (P2P – Layer 2/ E2E – Layer 2)
Traffic Management
- Multicast Frame Filtering
- Switching Portmask: User-defined forwarding of frames to concrete ports
- Port-based VLAN support
- QoS
- Priorities (PCP-802.1p, DSCP TOS, Ethertype)
- IEEE 802.1X EAPOL hardware processing
- DSA (Distributed Switching Architecture) tagging: The ideal case for using DSA is when an Ethernet switch supports a “switch tag” which is a hardware feature making the switch insert a specific tag for each Ethernet frames it received to/from specific ports to help the management interface figure out:
- What port is this frame coming from
- What was the reason why this frame got forwarded
- How to send CPU originated traffic to specific ports
Configuration
- MDIO, UART, AXI4-Lite or CoE (Configuration-over-ethernet) management interfaces
- Configuration-over-Ethernet (COE): Full access to internal registers through the same Ethernet link that connects to the CPU
- Drivers are provided with IP Core purchase
Redundancy Protocols
- RSTP (Software stack required)
- Hardware support for RSTP
- Reference RSTP stack for Linux provided with the IP Core
- Posix Compatible RSTP stack available
- MRP (Software stack not required)
- Ring Manager (MRM)
- Ring Client (MRC)
- DLR (Software stack not required)
- Beacon Based Node
- Supervisor Node
- HSR (Software stack not required)
- Edition 3.0 (Latest)
- PRP (Software stack not required)
- Edition 3.0 (Latest)
- Multiple HSR mode supported
- Supported PRP modes: Duplicates Discard, Duplicates Accept
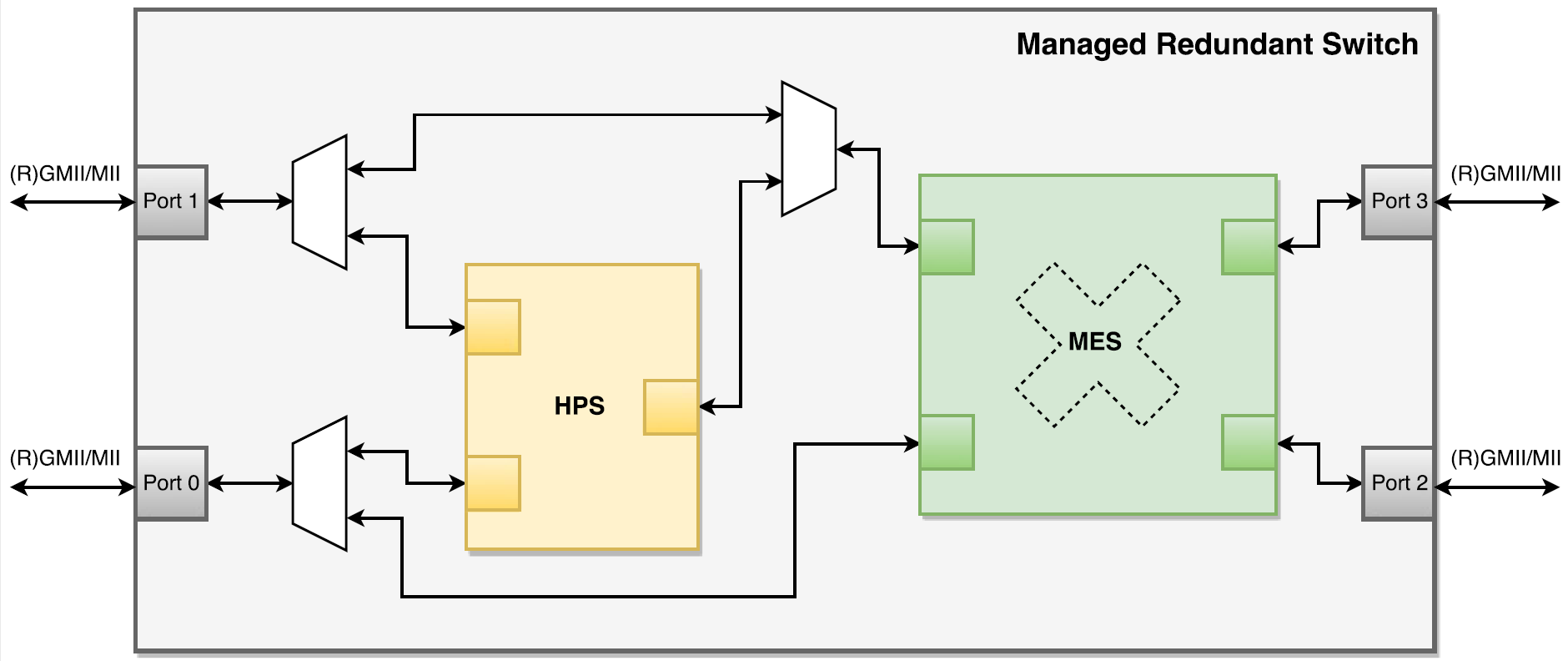
- Managed Redundant Switch IP Core block diagram -
Supported boards for the Reference Designs:
- SoC-e SMARTzynq brick
- For other Xilinx/Avnet/SoC-e boards, we can provide a time-limited IP Core for evaluation.
